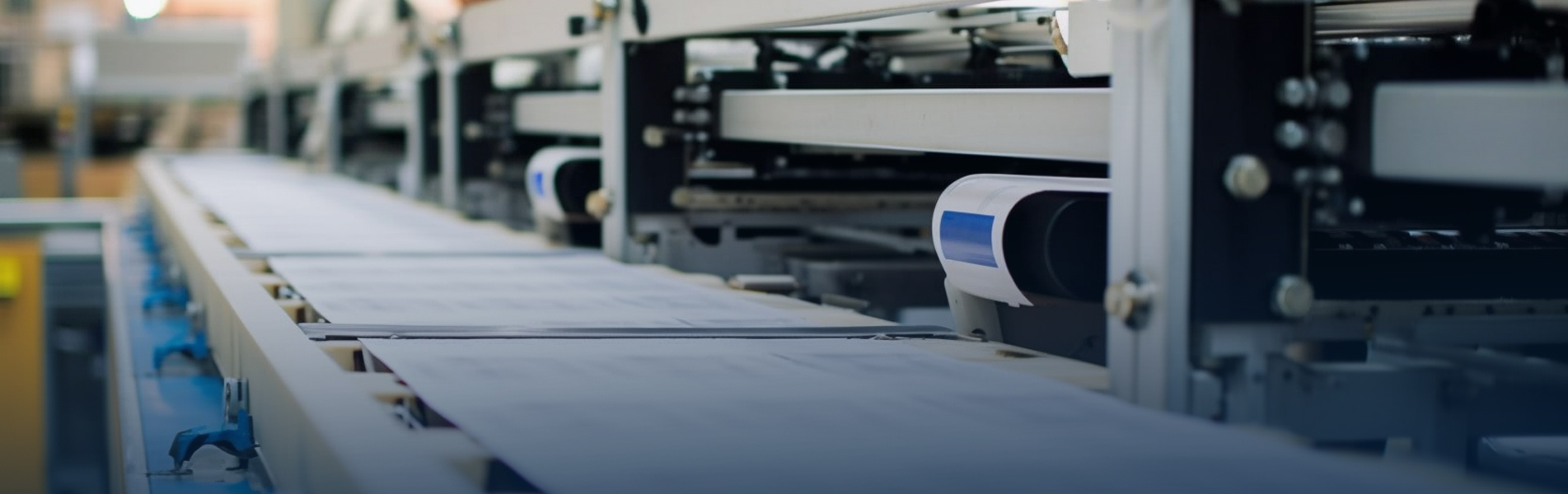
In today's rapidly changing electronics industry, ceramic substrate materials as a key basis for supporting high-performance electronic devices, its performance and characteristics directly affect the overall performance and reliability of electronic products. From the early alumina ceramics to the later aluminum nitride, silicon nitride and other new materials, the development of ceramic substrate materials has witnessed the continuous progress and innovation of science and technology. This article will take you to explore the unique advantages and application prospects of these ceramic substrate materials, especially how aluminum nitride and silicon nitride ceramics stand out in the solution of high-power device heat dissipation and high-intensity heat dissipation environment with their excellent performance, and become an indispensable important material in the modern electronics industry.
Alumina substrate, as the pioneer of ceramic substrate, has been successfully developed by Siemens in Germany since 1929 and entered industrial production in 1933, with its low price, excellent stability, good insulation and mechanical properties, has long occupied a dominant position in a wide range of applications. However, its relatively low thermal conductivity and thermal expansion coefficient that do not match Si limit its further development in high-power electronic products, and it is mainly used in the field of low-voltage and low-integration circuit packaging.
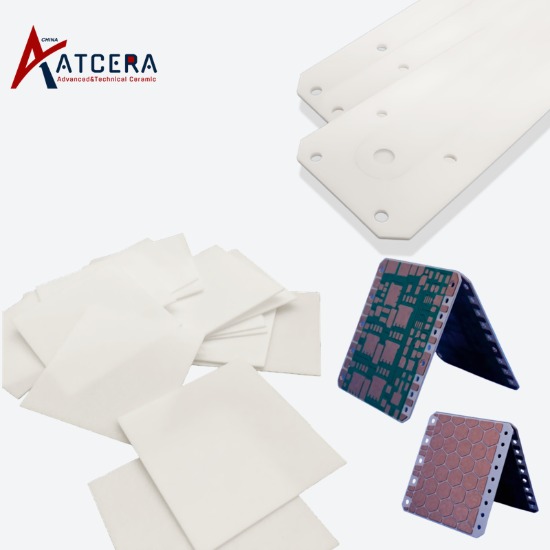

Subsequently, although BeO substrates stood out for its high thermal conductivity, the toxicity problem became an insurmountable obstacle, which was not only banned in Japan, but also severely restricted in Europe, greatly hindering its wide application.

In contrast, although the SiC single crystal has an amazing thermal conductivity, the thermal conductivity of polycrystalline SiC ceramics decreases significantly due to the difference in grain orientation, coupled with poor insulation performance and high dielectric loss, which makes the research progress in the field of circuit board materials slow.
Under this background, aluminum nitride and silicon nitride ceramics are gradually emerging with their unique performance advantages. Aluminum nitride substrate with its excellent high thermal conductivity (theoretical value up to 320W/ (m·K), commercial product thermal conductivity is also between 180W/ (m·K) ~260W/ (m·K)) has become a key material to solve the heat dissipation problem of high-power devices, and since the 1980s, under the promotion of developed countries, especially Japan, It has rapidly developed into a new generation of advanced ceramic packaging materials. Its high mechanical strength and chemical stability ensure stable operation in harsh environments.

Silicon nitride substrates, after experiencing the early stage of underestimated thermal conductivity, through scientific research and process optimization, its thermal conductivity has been significantly improved, breaking through 177W/ (m·K), while maintaining a very low coefficient of thermal expansion (3.2×10−6/℃), becoming one of the most excellent ceramic substrate materials with comprehensive performance. Its excellent bending strength and wear resistance show extraordinary competitiveness in high intensity heat dissipation environment.
In summary, aluminum nitride ceramics are the best choice for heat dissipation of high-power devices due to their high thermal conductivity and thermal expansion coefficient matching semiconductor materials. Silicon nitride ceramics, with their comprehensive performance advantages, lead the way in demanding thermal environments. Together, the two lead the ceramic substrate materials to higher performance and a wider range of applications.




























